Getting Started
Since the rack does not have network access at this point, the initial setup is performed by connecting to the technician ports ('techport' in short) on the rack switches via a laptop or jumpbox set up with instructions from Oxide.
The software used for rack component visualization, update, and configuration is known as Wicket. This software runs inside the switch zones on the sleds adjacent to the switches, specifically sleds 14 and 16. Wicket provides a TUI and CLI that allow you to:
Validate component end-to-end connectivity
Update rack software to the latest versions, if necessary
Set up recovery account credentials
Upload a TLS certificate for the
recoverysiloConfigure basic networking such as upstream DNS, NTP, VLAN and routing information
To access a wicket captive shell,
First, identify the techport addresses with
ip neighbor show | grep fdb1
The output shows up to four sets of addresses and interfaces, one for each of the two techports on the two switches. If only one techport is connected to the laptop/jumpbox on each of the rack switches, the output may look like the following:
fdb1:a840:2504:195::1 dev eno2 lladdr 02:08:20:36:5c:8d REACHABLE fdb1:a840:2504:352::1 dev eno1 lladdr 02:08:20:bb:26:4d REACHABLE
Select any of the techport addresses and ssh in as the wicket user
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS}for example,
ssh wicket@fdb1:a840:2504:195::1
This should give you an Oxide splash screen and land you in wicket showing a graphical display of the rack.
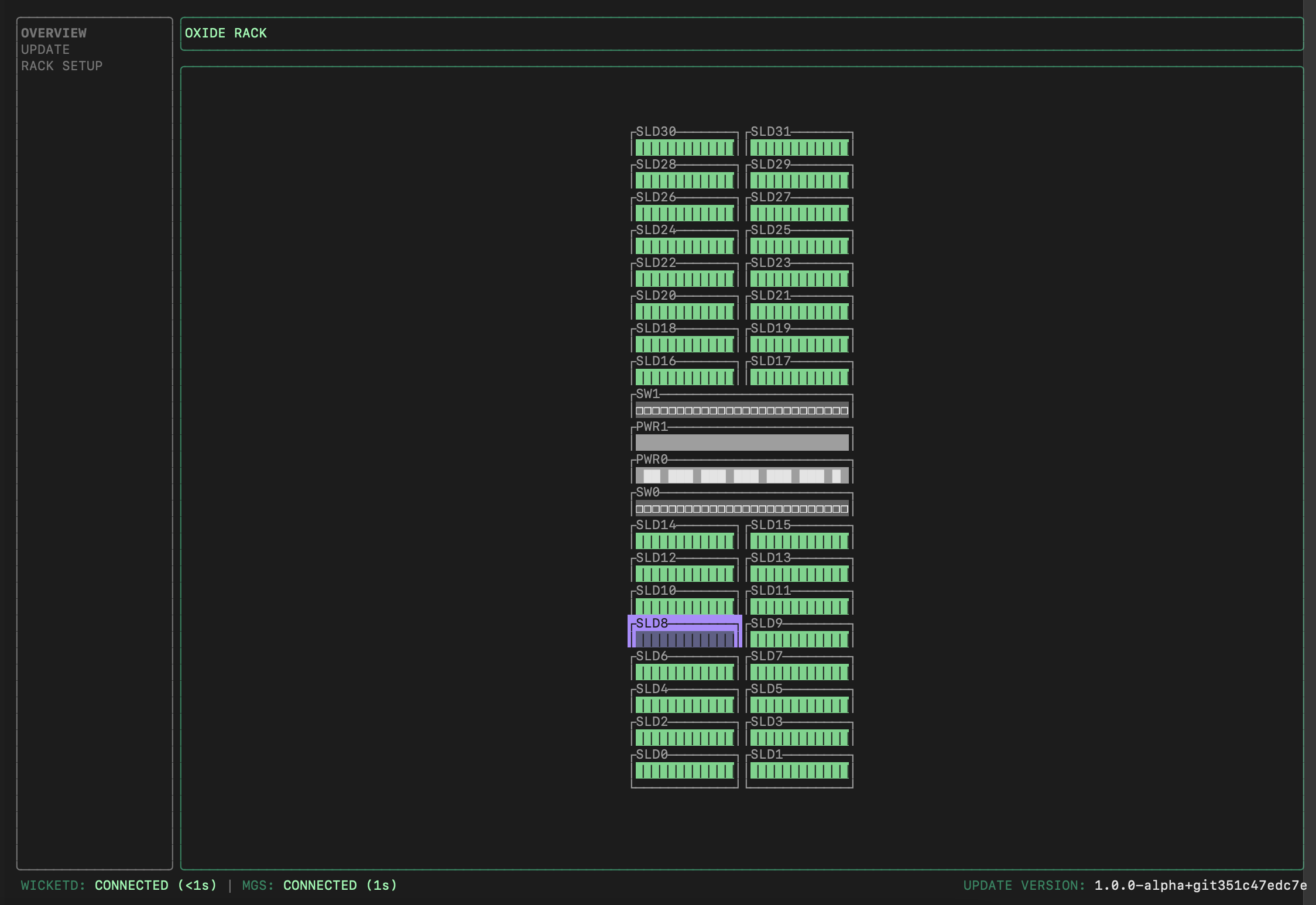
Validate component connectivity
Wicket communicates with the Management Gateway Service (MGS) to retrieve information about sled position and identity from the Service Processors (SP) in each Sled, Switch, and Power Shelf Controller (PSC).
To view the sled and switch information:
On the left pane of the wicket UI, you can use the up and down arrows (or
j/ka la vim) to select a screen.Select
OVERVIEWand pressTabto move focus into the rack. For every sled displayed, you can pressEnterto see its details.On the sled detail screen, you can use left and right arrows (or
h/l) to move left and right.
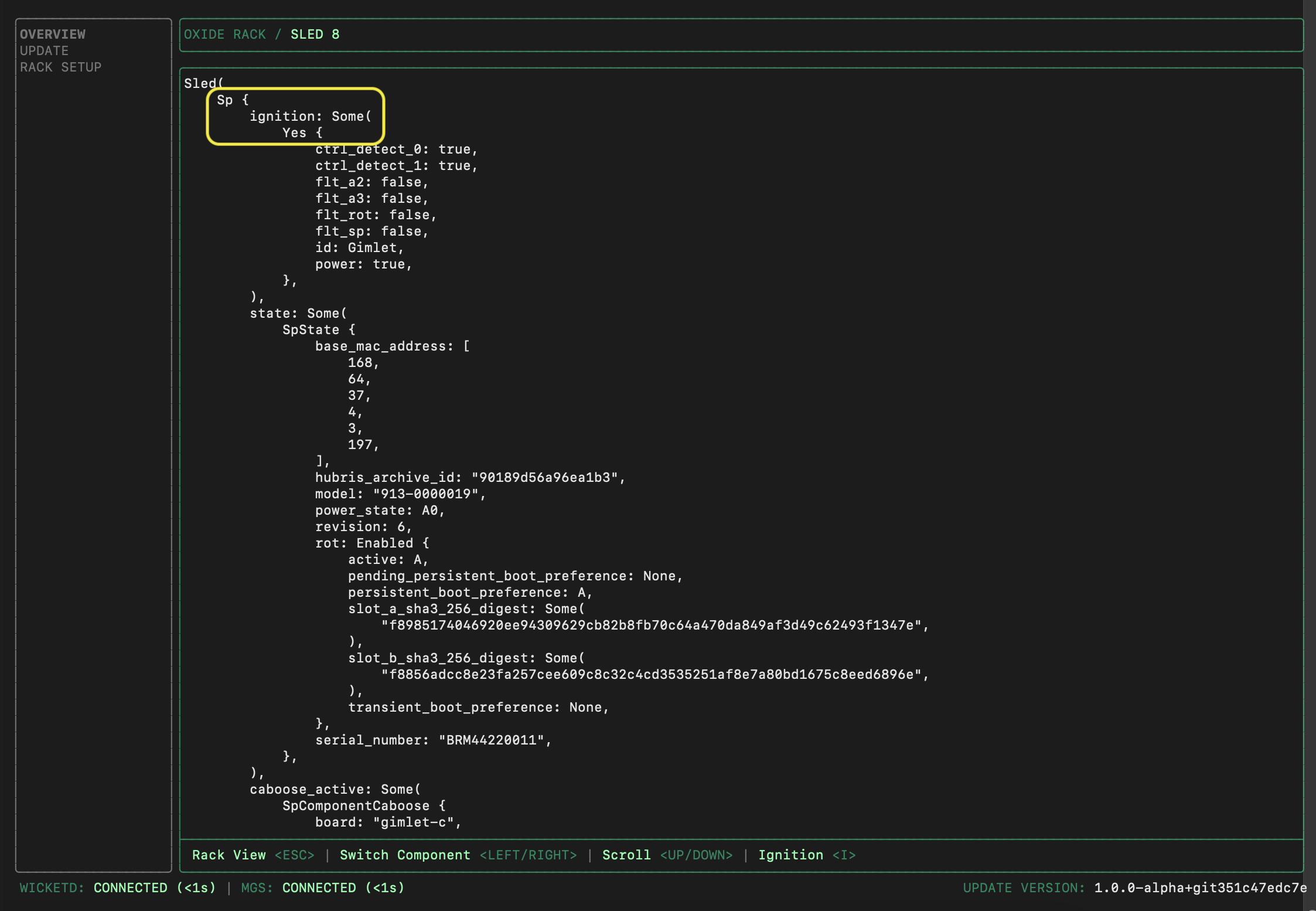
Confirm that the number of sleds with Ignition information matches the expected count (16 for a half-rack, 32 for a full rack), and that the two switches and PSC(s) are all powered on.
Verify uplink location and signal quality
While still in the wicket OVERVIEW section, review the transceiver status for both Switch 0 and Switch 1 (the information can be found towards the bottom of the switch details page):
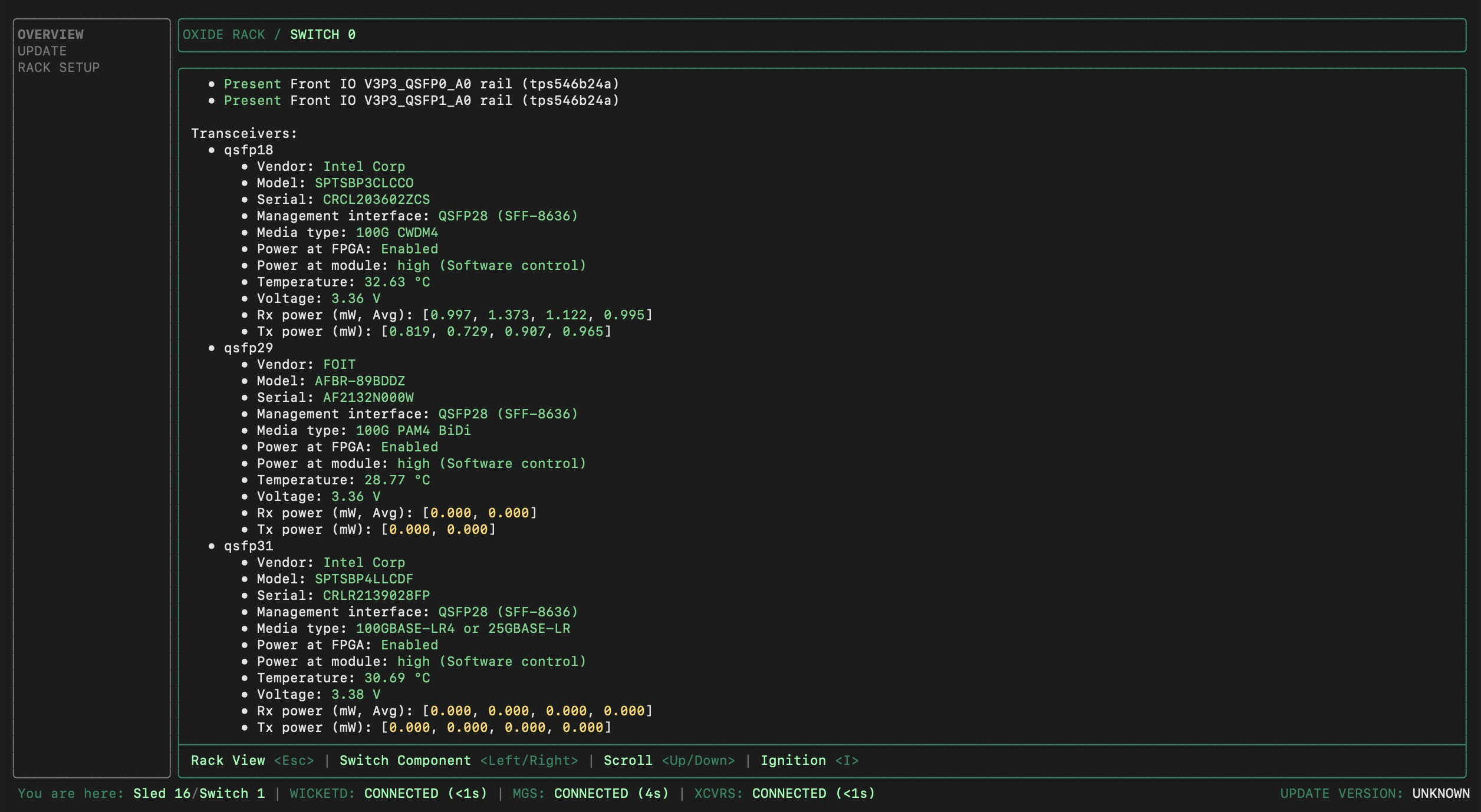
Check QSFP port assignments
Ensure the transceiver QSFP port numbers match the ones expected.
Correct the physical connections as needed.
Check power levels
Verify that detected power levels are within expected ranges:
Rx power values should be between 0.7 - 1.5mW for active channels. (Note: For FR1 or SR1, only channel 1 is applicable; channels 2-4 will show 0.000.)
Tx power values are zero at this point, because the uplinks are not set up yet.
Power at module should be labeled as "high".
Any values highlighted in yellow indicate an abnormal condition, with the exception of the Tx power as noted above. If Rx power values are 0.000 but some Tx power values are non-zero, this may indicate swapped rx/tx cables.
Check for temperature/voltage anomalies
Wicket provides environmental readings that may indicate potential issues.
If Temperature or Voltage appears in yellow, do not proceed with rack setup, even when the transceivers detect light and power levels appear normal.
After completing the checks, exit wicket by pressing Ctrl-C.
Update rack software
The software on the Oxide rack may require updates if there are newer releases post-shipment. Software updates are performed only by Oxide technicians at this time, onsite or remotely via a secure jumpbox connected to the rack.
The switches and their adjacent sleds are updated one set at a time so that there is always a live wicket to drive the process:
use the Sled 16 wicket to update Switch 0 and its adjacent Sled 14
use the Sled 14 wicket to update Switch 1, PSC(s), and remaining sleds
Each step takes about 30 minutes in which multiple system components are updated concurrently. For each of the steps:
First, upload the software image zip file to the target wicket with the following command
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} upload-repo < tuf-mupdate.zipNext, ssh into wicket
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS}Then, initiate the update from wicket UI
On the left pane of the wicket UI, select
UPDATEand pressTabto move focus into the rack.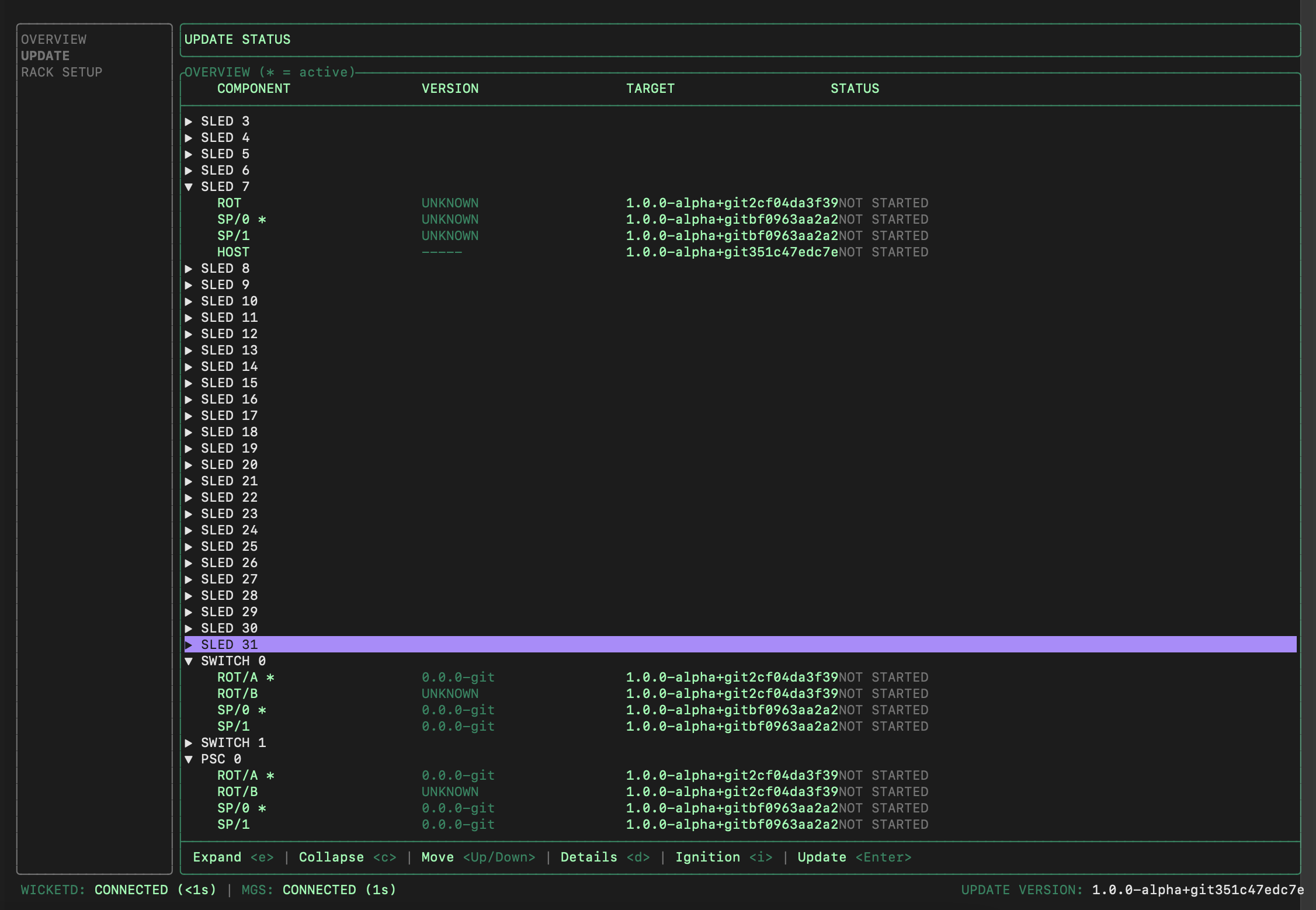
Arrow down to the target sled. You can press the right/left arrows to expand or collapse the short list of versions (there should be only one version available during the first rack install).
Press
Enterand this should take you to another pane with the versions listed at the top, and the bottom should say "Update ready: pressCtrl-Uto start".Press
Ctrl-U, then pressYon the popup to confirm you want to start the update. The bottom pane will be replaced by a list of steps that will be performed.

At any time, you can move up and down the list (via up/down/j/k) and press enter to see details about the step. The sleds will be rebooted automatically after update. Here is an example of the update step details:
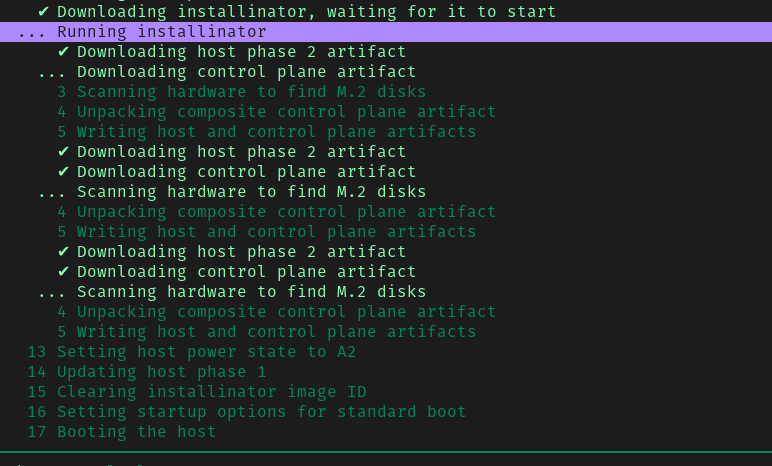
Once all the components have completely booted up, the rack is ready for network configuration.
Configure Rack Settings
Launch wicket UI via any of the available techport interfaces
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS}On the left pane, select RACK SETUP. The current rack status displayed on the right pane will be "Uninitialized" at this point.
While keeping the wicket UI open, start another terminal session and ssh into the setup command shell:
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setupThis should bring up the list of available subcommands:
Usage: wicket setup [OPTIONS]Commands: get-config Get the current rack configuration as a TOML template set-config Set the current rack configuration from a filled-in TOML template reset-config Reset the configuration to its original (empty) state set-password Set the password for the recovery user of the recovery silo set-bgp-auth-key Set one or more BGP authentication keys upload-cert Upload a certificate chain upload-key Upload the private key of a certificate chain help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
In this second terminal window, you will make use of the commands above to enter or upload the necessary rack configurations.
Set Recovery User Password
A built-in recovery silo (with a system user also named recovery) will
be created by the rack initialization process for setup and recovery purposes.
This is an ordinary silo backed by a local identity provider. The recovery
user has the privileges to create other silos and modify mutable pieces of their
identity provider configuration.
Execute the following subcommand to enter the password for this system user:
ssh -t wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setup set-passwordUpload TLS Certificate
Oxide Console and API will be hosted under the domain name controlled by your
organization. In this step, you will upload a TLS certificate and private
key that corresponds to the subdomain delegated to the Oxide Rack. This TLS
certificate is used for the recovery silo but generally a TLS certificate
with a wildcard DNS SAN is generated so it can be used for user-created silos
as well.
For example, given a delegated DNS name of cloud.acme.com one can generate
a TLS certificate with a DNS SAN of *.sys.cloud.acme.com to use it for both
the recovery silo (i.e., recovery.sys.cloud.acme.com) and user-created
silos (i.e., silo01.sys.cloud.acme.com). Alternatively, one could generate
a TLS certificate with a DNS SAN specific to each silo but that would have to be
done each time a new silo is created.
With a TLS certificate in hand, execute the upload-cert subcommand to import
the TLS certificate chain file:
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setup upload-cert < ${CERT-CHAIN}.pemand then upload-key to import the key file:
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setup upload-key < ${CERT-KEY}.pemConfigure basic networking
In this step, you will configure the endpoints of boundary services that integrate with the Oxide Rack. You will supply the information in the form of a text file in toml format.
To begin the configuration, retrieve the toml template via
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setup get-config > rack.tomlThe content of the file should look like this:
# Delegated external DNS zone name
#
# The rack provides separate external API and console endpoints for each Silo.
# These are named `$silo_name.sys.$external_dns_zone_name`. For a Silo called
# "eng" with delegated domain "oxide.example", the API would be accessible at
# "eng.sys.oxide.example". The rack runs external DNS servers that serve A/AAAA
# records for these DNS names.
external_dns_zone_name = ""
# IP addresses for authoritative external DNS servers operated by the rack for
# the DNS domain delegated to the rack by the customer. Each of these addresses
# must be contained in one of the "internal services" IP Pool ranges listed
# below.
external_dns_ips = [
]
# External NTP servers; e.g., "ntp.eng.oxide.computer".
ntp_servers = [
]
# External DNS server IP Addresses; e.g., "1.1.1.1", "9.9.9.9".
dns_servers = [
]
# Ranges of the service IP pool which may be used for internal services.
#
# Elements of this list should be of the form:
#
# { first = "first_ip", last = "last_ip" }
#
# where `last_ip` is equal to or higher than `first_ip`; e.g.,
#
# { first = "172.20.26.1", last = "172.20.26.10" }
internal_services_ip_pool_ranges = [
]
# List of sleds to initialize.
#
# Confirm this list contains all expected sleds before continuing!
bootstrap_sleds = [
(list of sleds auto-discovered from the rack will be displayed here)
]
# Allowlist of source IPs that can make requests to user-facing services.
#
# Use the key:
#
# allow = "any"
#
# to indicate any external IPs are allowed to make requests. This is the default.
#
# Use the below two lines to only allow requests from the specified IP subnets.
# Requests from any other source IPs are refused. Note that individual addresses
# must include the netmask, e.g., "1.2.3.4/32".
#
# allow = "list"
# ips = [ "1.2.3.4/5", "5.6.7.8/10" ]
[allowed_source_ips]
allow = "any"
# network config
[rack_network_config]
infra_ip_first = ""
infra_ip_last = ""
# A table of ports to initialize on the rack. The keys are the switch (switch0,
# switch1) and the port name (qsfp0, qsfp1, etc). Copy and paste this section
# for each port.
[rack_network_config.switch0.qsfp0]
# Routes associated with this port.
# { nexthop = "1.2.3.4", destination = "0.0.0.0/0" }
routes = []
# Addresses associated with this port.
# "1.2.3.4/24"
addresses = []
# `speed40_g`, `speed100_g`, ...
uplink_port_speed = ""
# `none`, `firecode`, or `rs`
uplink_port_fec = ""
# Whether or not to set autonegotiation: `true` or `false`
autoneg = false
# A list of BGP peers for this port. Copy this section, changing the port name
# as desired. Remove if not needed.
[[rack_network_config.switch0.qsfp0.bgp_peers]]
# The autonomous system number (required). This must match one of the `asn`
# values in the `[[rack_network_config.bgp]]` section.
asn = 0
# The switch port the peer is reachable on (required).
port = ""
# The IPv4 address of the peer (required): e.g. 1.2.3.4.
addr = ""
# How long to keep a session alive without a keepalive, in seconds.
hold_time = 6
# How long to keep a peer in idle after a state machine reset, in seconds.
idle_hold_time = 3
# How long to delay sending open messages to a peer, in seconds.
delay_open = 0
# The interval in seconds between peer connection retry attempts.
connect_retry = 3
# The interval to send keepalive messages at, in seconds.
keepalive = 2
# Require that a peer has a specified ASN (optional).
# remote_asn = 0
# Require messages from a peer have a minimum IP time to live field (optional).
# min_ttl = 0
# If BGP authentication is desired, a key identifier. Multiple peers
# can share the same key ID, if desired.
#
# The actual keys are provided via `wicket setup set-bgp-auth-key`.
# Currently, only TCP-MD5 authentication is supported.
# auth_key_id = "key1"
# Apply the provided multi-exit discriminator (MED) for updates sent to the
# peer (optional).
# multi_exit_discriminator = 0
# Include the provided communities in updates sent to the peer (optional).
# communities = [28, 47]
# Apply a local preference to routes sent to the peer (optional).
# local_pref = 0
# Enforce that the first AS in paths received from the peer is the
# peer's AS.
enforce_first_as = false
# Apply import policy to this peer with an allowlist of prefixes
# (optional). Defaults to allowing all prefixes. Use an empty list to
# indicate that no prefixes are allowed.
# allowed_import = ["224.0.0.0/8"]
# Apply export policy to this peer with an allowlist of prefixes
# (optional). Defaults to allowing all prefixes. Use an empty list to
# indicate that no prefixes are allowed.
# allowed_export = []
# Associate a VLAN ID with this BGP session (optional).
# vlan_id = 0
[rack_network_config.switch1]
# Optional BGP configuration, as a list of entries. Duplicate or remove this
# section as needed.
[[rack_network_config.bgp]]
# The autonomous system number.
asn = 0
# Prefixes to originate e.g., ["10.0.0.0/16"].
originate = []internal_services_ip_pool_ranges are used for Control Plane DNS and API services. The pool range(s) must cover 16 or more IP addresses.qsfp0 with the actual qsfp port in use for uplink connection.Use a text editor such as vim to edit the toml file. Upon completing the configuration data entry, you can upload the file via
ssh wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setup set-config < rack.tomlThe configurations should be refreshed automatically in the wicket UI with the uploaded data. If everything looks correct, proceed to the next step; else, edit the configurations with reset-config, get-config, and set-config as needed.
Specify VLAN tag
If you use VLAN tagging for the control plane or data plane, you will need to configure the VLAN tag in the switch port settings. Here is an example:
[rack_network_config.switch.qsfp31]
uplink_port_speed = "100G"
uplink_port_fec="none"
autoneg = false
# for tagged control plane traffic
addresses = [{address = "198.51.103.10/30", vlan_id = 100}]
# for tagged data plane traffic
bgp_peers = [
{asn = 47, addr = "198.51.103.9", port = "qsfp31", vlan_id = 100},
]
routes = []Enter BGP auth key values
If your network configurations do not involve BGP authentication, you can skip to the next step to start rack initialization.
You will reference the auth_key_id entered in the toml file uploaded in
set-config to specify the keys associated with each of the key ids.
For example, for the following BGP peer:
[[rack_network_config.switch0.qsfp31.bgp_peers]] asn = 47 addr = "198.51.103.9" port = "qsfp31" local_pref = 20 auth_key_id = "bgpkey"
you can set the password associated with that key as follows:
$ ssh -t wicket@${TP_ADDRESS} setup set-bgp-auth-key 'bgpkey'
current BGP authentication keys (0/1 set):
• bgpkey: unsetYou will then be prompted for a password. Upon filling in the password you’ll see something like this (with a different SHA-256).
setting 1 key to use TCP-MD5 authentication
• (1/1) add bgpkey:
✓ key added: TCP-MD5 (SHA-256: 650e9595236154547665929c8ff6c06a4e1f89bb63797649b3cfc5337d075be8)
✓ 1/1 key set
Connection to fdb1:a840:2504:2d7::1 closed.The auth key pairs entered will also be reflected in the rack configurations displayed in the wicket UI.
Kick off rack initialization
Review the rack configurations in the wicket UI. If everything looks correct,
you can kick off the rack setup by pressing Ctrl-K. The process takes about
15-20 minutes. Once the initialization has completed, the Current rack status
will become Initialized. Here is an example of the final state:
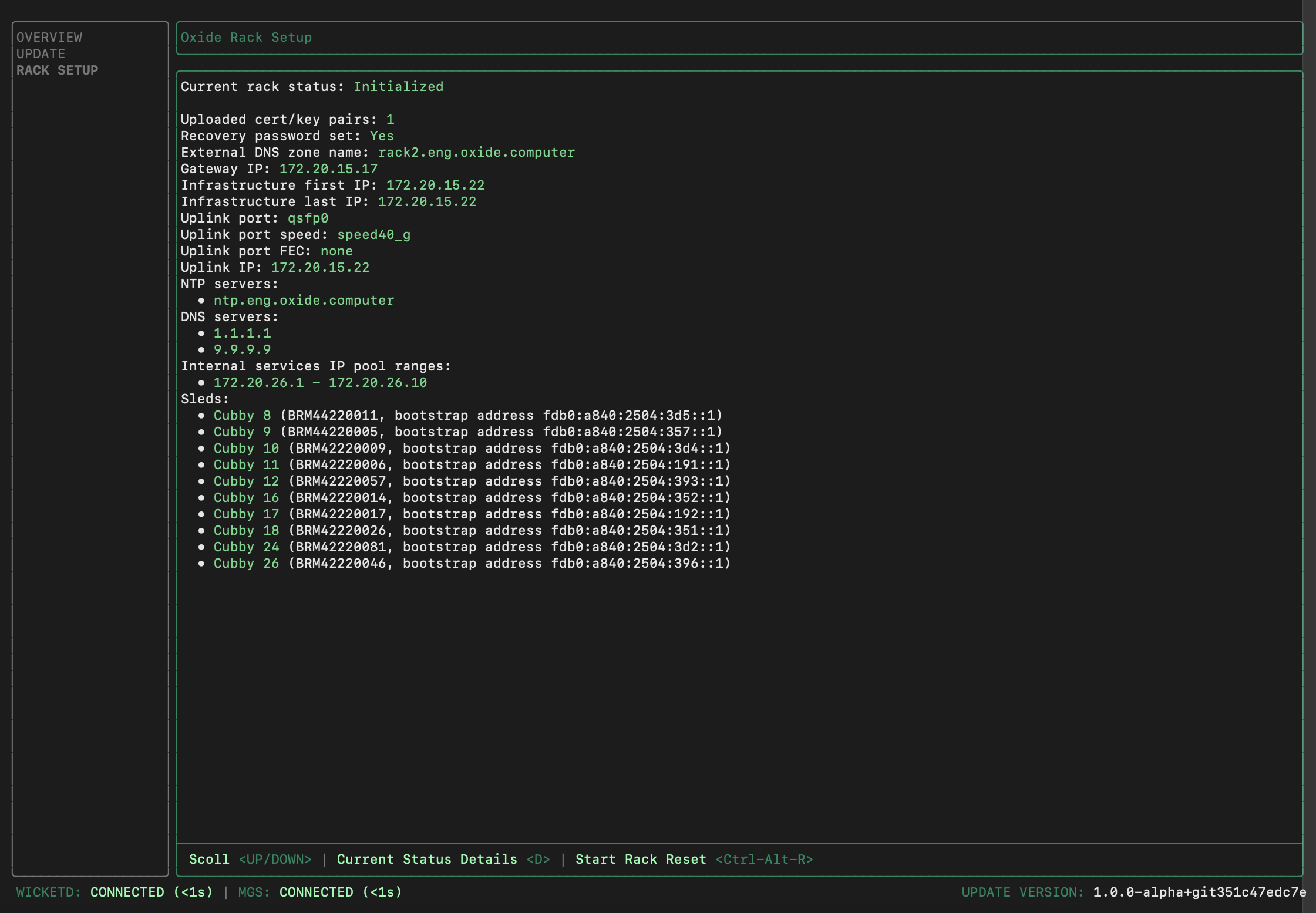
Contact Oxide Support if the rack initialization does not run to completion or shows a failed status.
Next: Log in the web console to complete the rest of the rack configuration.