Silos are the top-level containers for users, projects, and resources, ensuring strict tenancy separation. Users can only see resources in their own silo. Each silo has its own resource limits and access policies as well as its own subdomain for the web console and API. You can choose to set up one or multiple silos depending on your organization’s resource and access management policies.
Rack administrators and users are typically onboarded into silos via identity provider (IdP) integration. Silos can also be configured to have rack-local accounts, which authenticate with username and password and must be created manually by silo administrators.
Recovery silo
A special silo called recovery is created during rack setup. The silo hosts a system account which is also named recovery. This built-in account has the fleet admin role that allows the operator to create user-defined silos and grant the fleet admin privilege to other users. After the rack setup process, the recovery silo will only be used for rescue purposes such as remediating identity provider integration configuration problems.
Silos vs. Projects as Tenants
Both silos and projects can be used as the abstraction for tenants. While projects provide some separation between different application workloads, when the tenant is in an entirely different security domain (e.g., a subsidiary or a third-party company), it may be more appropriate to give them their own silo so they are fully isolated.
Preparations for Silo Setup
Generate a TLS Certificate
A TLS certificate is required during silo setup and will be used for TLS termination on the silo-specific UI/API DNS name. The certificate’s DNS SAN can either be the silo’s fully-qualified domain name (FQDN):
$siloName.sys.$oxideDomainNameor a wildcard domain name:
*.sys.$oxideDomainNameConfigure Identity Provider
Oxide supports the use of SAML SSO authentication with third-party identity provider systems. User and group provisioning can be configured to be just-in-time (JIT) or synchronized real-time using SCIM 2.0 API. More information about the different types of authentication and authorization setup can be found in the Identity Providers guide.
Before setting up the IdP integration for a silo, you will need to identify the IdP group, role, or attribute to be used for governing memberships of the new silo and users who are designated as administrators.
Determine which IP pools to use
You may configure the new silo to have its own IP pools or use existing pools for external IP and multicast address assignment. If you choose to provide the silo with new IP pools, you will create the pools and allocate IP ranges to them prior to setting up the silo. If the new silo will be using existing pools, you may need to review the size of those IP pools and add capacity as needed.
You can find out more about IP pools in the IP Pools guide.
Determine Resource Limits
Virtual compute and storage resources such as vcpus and virtual disks make use of physical resources in the rack. They are shared among users of different silos. To ensure individual silos can get the resources guaranteed to them, you will establish the appropriate resource limits as part of the silo setup. Currently there are three kinds of resource quotas: vcpu, memory, storage. Their utilization calculations are defined as follows:
vcpu, in number of cores: utilization = (aggregated ncpus of powered-on instances owned by the silo) / (silo vcpu quota)
memory, in Gibibytes: utilization = (aggregated memory size of powered-on instances owned by the silo) / (silo memory quota)
storage, in Gibibytes: utilization = (aggregated size of disks and snapshots owned by the silo) / (silo storage quota)
running, starting, stopping, and rebooting.The sum of the silo quotas should ideally be below the total usable rack capacity to avoid over-provisioning. If silo quotas are set above the rack capacity and an instance or disk request cannot be accommodated by any sleds in the rack, the rack-level capacity check will kick in to reject the request. The current maximum usable capacity for instances and disks are:
Resource type | Memory* | Storage |
|---|---|---|
Per sled | 869,498,093,568 bytes (809 GiB) | 27,298 GiB (26.6 TiB) |
Half-rack | 12,944 GiB (12.6 TiB) | 436,768 GiB (426.5 TiB) |
Full-rack | 25,888 GiB (25.2 TiB) | 873,536 GiB (853.0 TiB) |
*The memory capacity listed is for sleds with 1 TiB DRAM. For sleds with 2 TiB DRAM, the usable memory is 1667 GiB per sled.
It is a best practice to always maintain capacity utilization of an Oxide rack below 70%. Apart from resources consumed by the systems software, there are other conditions that require a 15-30% buffer of compute resources:
Instance placement currently follows a random sled selection strategy. This reduces the risk of application outage when instances are spread across different sleds. The strategy may, however, result in the inability to place a large instance when all sleds are relatively full. If you have large instances that are dynamically brought up and down, you may want to reserve a larger percentage of unallocated compute resources.
Usable capacity may also be reduced when some of the sleds are taken out of service due to planned maintenance (e.g., software update) or unplanned outage.
Storage resources may be subject to contention to a lesser extent. The usable capacity represented in the system utilization view takes into account the 3x data replication factor and a fixed percentage overhead for snapshots and images.
Setting up a Silo
The procedures for setting up new silos and identity provider integration are similar to those during rack initialization. Operators who have the fleet-admin role can use the Oxide Console, API, or CLI to create a new silo and configure its resource and integration settings.
1. Create Silo and Upload TLS Certificate
The first step of silo setup is creating the silo record and importing a matching TLS certificate. Virtual resource quotas are required during silo creation and can be modified afterwards. Please refer to the Create a User Silo section for all the attributes involved and an example API request.
2. Create identity provider (optional)
Perform this step only if your silo integrates with an external identity provider (IdP).
In this step, you’ll create the IdP configuration to integrate Oxide rack user authentication and authorization with the provider. See the Identity Providers guide for detailed specifications and integration examples.
You can verify the IdP setup by logging into the Oxide console as any of the users in the silo admin group specified in the IdP configuration. The new silo URL will be at: https://$siloName.sys.$oxideDomainName/.
3. Create silo administrator account (optional)
Perform this step only if your silo uses the local authentication mode. An example of the API requests for creating the user account and granting administrator access can be found at Create Local Users.
4. Configure access control policies (optional)
If the silo is set up for IdP integration, the admin role is automatically granted to members of the Admin group name specified during silo creation.
You may grant other access levels via the collaborator and viewer roles to other users via the Console, API, or CLI.
5. Link silo to IP pools
Each silo can be linked to one or more IP pools and one of them should be marked as the default. Only linked IP pools can be used for automatic address assignment when ephemeral or floating IPs are created for VM instances.
6. Configure access token expiration (optional)
Tokens generated for API and Console sessions are set to never expire by default. You can override the setting with the /v1/auth-settings API (the setting will be available on the Console in a future release). Token expiration is specified in the form of token lifetime or time-to-live (TTL), not a certain system time. As an example, if you make it 3600 seconds, new tokens will be set to expire one hour from their respective creation times.
Changes in TTL only take effect on tokens created after the fact. Existing tokens will still be revoked based on the original expiration dates set during creation. More enhancements will come in future releases to allow administrators to configure the TTL of Console session tokens and to expire tokens on behalf of other users.
Related API Reference
The following APIs are accessible to fleet administrator only:
scim_token_* endpoints to manage SCIM tokens for their own silo, while fleet administrators can manage tokens across all silos.Silo Resource Quota Management
The vcpu, memory and disk resources allowed for a silo can be adjusted up or down any time. Modifying quotas to levels below the current utilization does not impact resources already in use. The new limits only take effect when users attempt to make new instances, disks, or snapshots. Here are a few CLI examples for modifying resource quotas:
oxide silo quotas update --silo $siloName --cpus $vcpuCount --memory $memoryInBytes --storage $storageInBytes # To view the current quota and utilization of a certain silo oxide silo quotas view --silo $siloName # To view the current quota and utilization of all silos oxide silo utilization list
Related API Reference
The following APIs are accessible to fleet administrator only:
Silo Administrator Capabilities
Silo Resource Access
Silo administrators can access and act on all the child resources within the silo, including projects, instances, images, disks, snapshots, and VPCs. They can also modify the access policies of the projects to grant or revoke access permissions.
Silo administrators can view the capacity allocated to the silo as well as the current resources utilization on the console
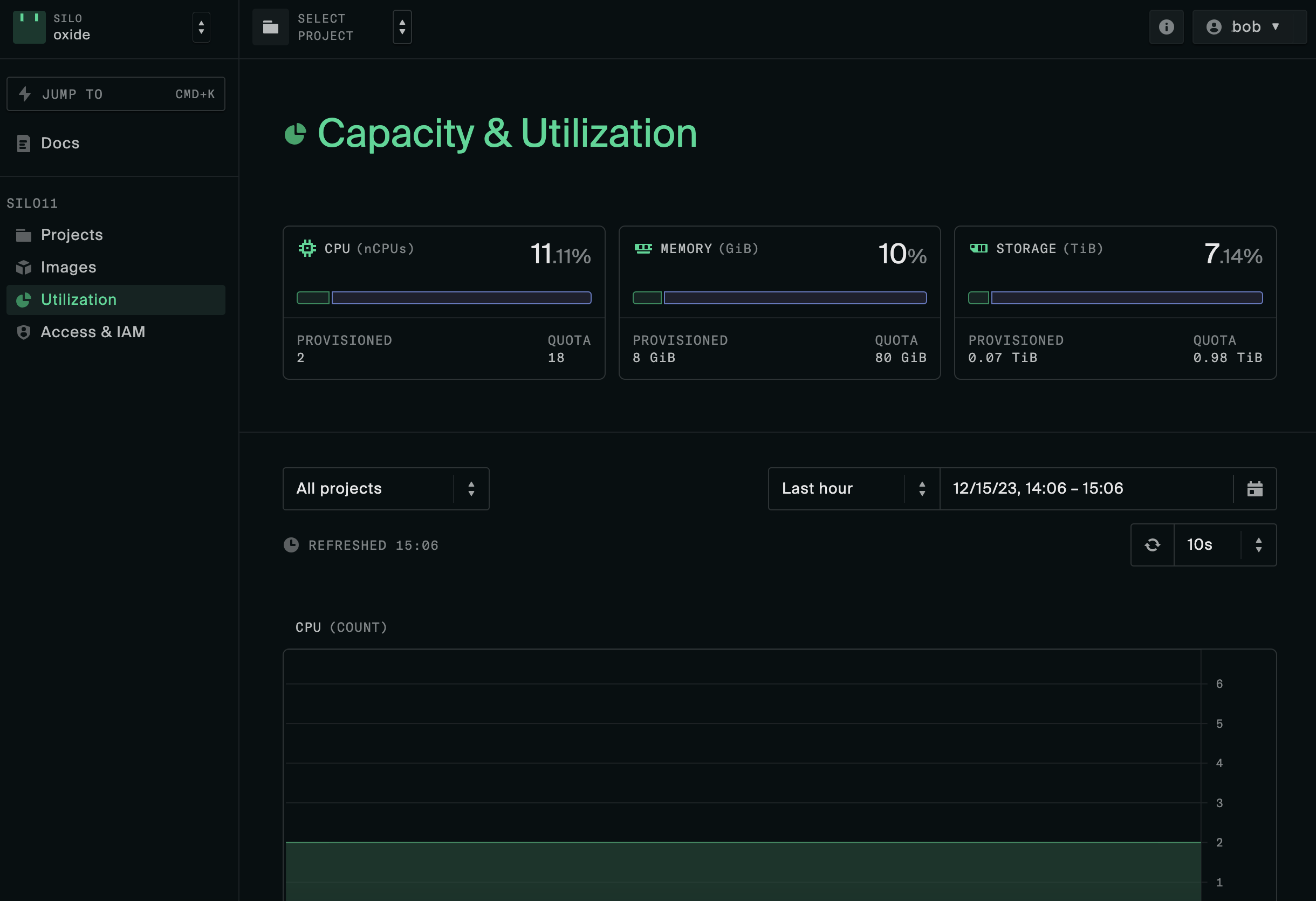
They can also see the available resources via the API:
When users attempt to provision more disks or start up more instances than permitted by the resource quotas or IP pools, they will receive an InsufficientCapacity error from the API. Silo administrators can either ask the fleet administrator to increase the resources allocated to the silo, or advise users in the silo to remove unused disks or running instances to free up compute, storage, and network resources.
Silo TLS Certificate Replacement
Silo administrators have the permission to manage TLS certificates for their silos.
To replace the existing TLS certificate for a silo:
If the administrator has access to more than one silo, first configure the
OXIDE_HOSTandOXIDE_TOKENenvironment variables that correspond to the target silo.Import the new certificate using certificate_create. Pass the
--insecureor-kargument if the existing certificate already expired.Remove the old certificate using certificate_delete.
sys subdomain in the DNS SAN (e.g., *.sys.$oxideDomainName). This is
necessary because silos are created as $siloName.sys.$oxideDomainName.Here are the API endpoints for managing TLS certificates:
Rotating Silo SCIM Tokens
Silo administrators have the permission to create new SCIM tokens and delete any unused ones through the Console or API.
The new token needs to be set in the SCIM app integration configurations of the identity provider before removing the existing one to avoid disrupting live user and group import.
Here are the API endpoints for managing SCIM tokens: